Transistor as a switch Circuit Diagram If the circuit uses the Bipolar Transistor as a Switch, then the biasing of the transistor, either NPN or PNP is arranged to operate the transistor at both sides of the " I-V " characteristics curves we have seen previously. The areas of operation for a transistor switch are known as the Saturation Region and the Cut-off Region. This means Transistor to Switch the LED. As discussed earlier, the transistor can be used as a switch. The schematic below shows how a transistor is used to switch the Light Emitting Diode (LED). When the switch at the base terminal is open, no current flows through the base so the transistor is in the cutoff state. Therefore, the transistor acts as an
Learn why transistors are used as switches in circuits and how to wire them up with examples. A transistor is a 3-pin device that turns on or off by electrical current and can also amplify signals.
Concept, Construction and Applications Circuit Diagram
Transistor as a Switch. Basically as per the generations of the electronic circuits gets revolutionized and improved for better and comfortable living the transistors played a prominent role by replacing themselves with vacuum tubes.. This leads to an improvement in efficiency and compression in size. The main functionality of the transistor can be observed either by making it be used for

Therefore, both the on - state and off - state power loss is zero in the transistor switch. Circuit Diagram of Transistor as a Switch Cut Off State (Open Switch) When transistor operates in the cut off region shows the following characteristics −. The input is grounded i.e. at zero potential. The V BE is less that cut - in voltage 0.7 V

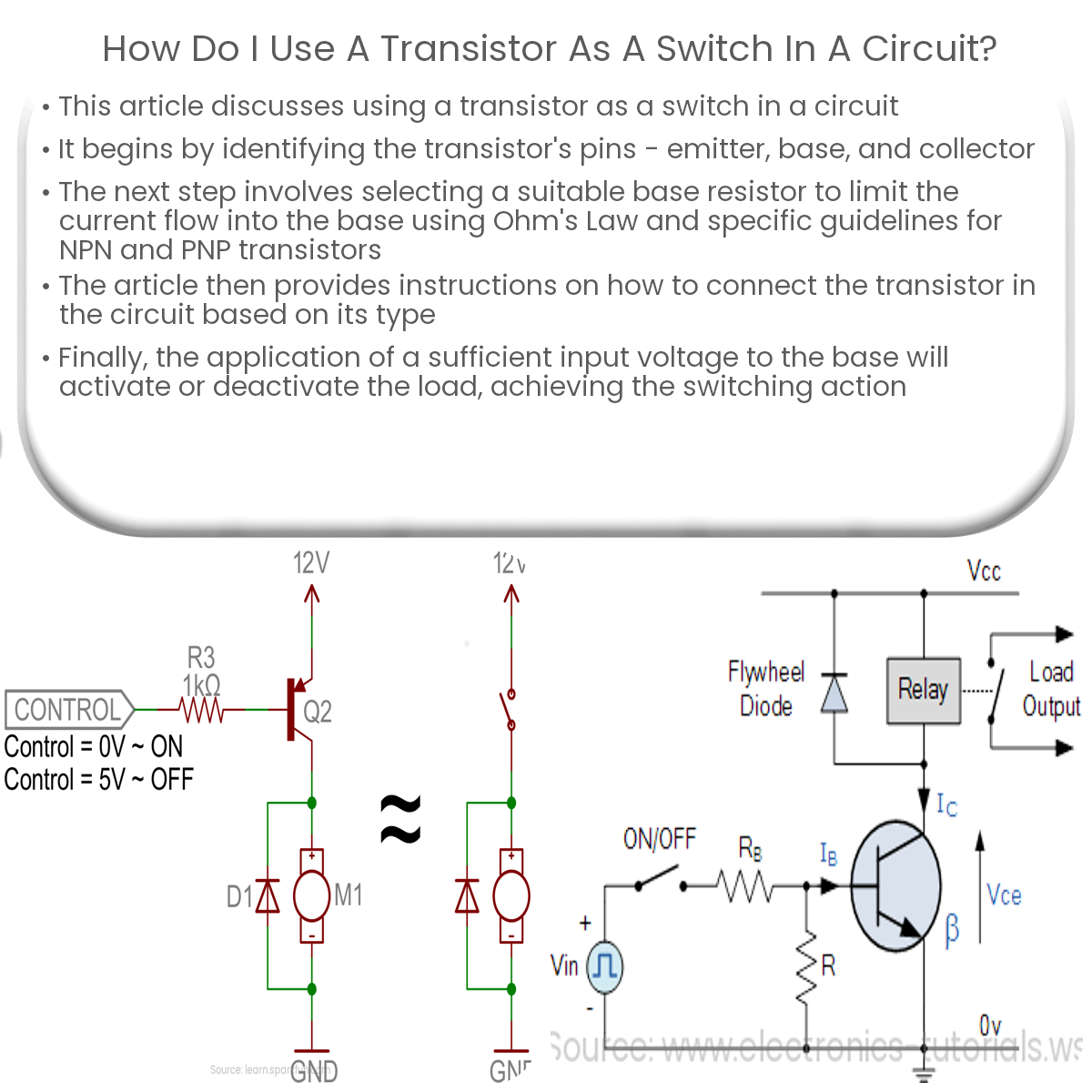
How to Connect a Transistor as a Switch in a Circuit Circuit Diagram
Many common-purpose transistors will only give you up to 100 mA. So for a current of 1A, it's important to choose a transistor that can handle it. The PNP Transistor as a Switch. A PNP transistor works the same way as an NPN transistor for switching operations, but the current flows in the opposite direction.
